Since I already defined the software stack as a whole, let define how things worked before the migration started.
How Sources and Dependencies are kept.
All the sources were in one big mono-repo. This repo defined engines that followed the definition of backend systems. So for each system (with all its services) we had a source project. Shared functionality was distributed through project libraries so that it could be pulled into multiple engines.
How to build stuff.
The CI pipeline used is Jenkins. Each time a check-in occurs, a Jenkins job is triggered to create a zip file containing the following definitions
- ems queues/topics
- File shares (required directories for testing)
- Database script
- EAR file for Tibco Administrator
- Files for local file system patches
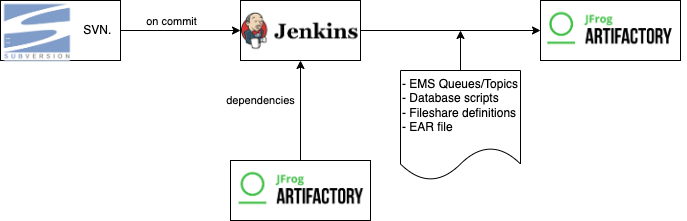
While this applies to any since engine, the need to define composites (multiple engines) arose early on. Composites are also defined by source repositories. These repositories consist only of versioned dependencies, but have no code of their own. This allowed us to reuse the existing pipelines and architecture.
How stuff is rolled out.
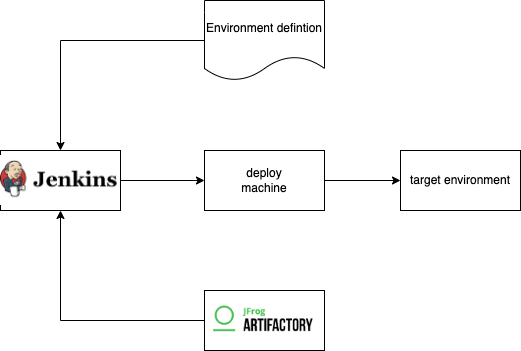
Each environment had its own definition file as a Jenkins job definition. This definition file contains settings such as
- Database url/credentials
- Tibco EMS url/credentials
- Tibco Administrator url/credentials
- Machine list (used for file rollout)
- Installed software list
- Additional feature list
- is DMZ supported
- Is set up as a cluster/single instance
- has regions
Using the Jenkins UI, we could first select an environment. Depending on the selected environment and therefore the features available on that environment, we could trigger tasks to be executed.
Tasks supported by our Jenkins jobs:
- Restart environment
- Deploy software (install/update EMS, BW, 3rd party components)
- Deploy single engine
- Deploy database script
- EMS definitions, queue, topics, bridges, routes
- Prepare file shares
- Deploy BW EAR via Administrator
- Perform file system rollout (e.g. SSL certificates, config files)
- Deploy composite (just a collection of multiple engines)